5.1 Our Environmental Management
For Madrileña Red de Gas, environmental protection has been a commitment since its creation as a company in 2010, being a pillar in the sustainable development objectives set by the Company. Overall compliance with the targets at the end of 2020 was 64%.
- Alignment with higher environmental ideals and values.
- Firm commitment to compliance with current legislation and other requirements to which the organization subscribes.
- Efficient management in the consumption of resources and energy saving.
- Prevention of pollution and minimization of the “environmental footprint” by controlling and progressively reducing the impact of our activities.
- Efficient and appropriate management of waste generated.
- Application of environmental criteria in our relations and commitments with customers, suppliers and contractors.
- Implementation of environmental sustainability strategies for continuous improvement through regular planning and monitoring of environmental objectives and targets.
- Promotion of internal environmental awareness, information and training activities.
In order to structure the application of this Environmental Policy, Madrileña Red de Gas has developed and maintains a UNE-EN ISO 14001:2015 management system, which forms part of the Integrated Quality, Environment and Prevention Management System (the system is currently being reviewed with the aim of carrying out an external audit in 2021 to renew the certification).
Currently, the objectives of the environmental management system are aligned with the focus of the ESG Gresb platform.
Madrileña Red de Gas has a methodology in place for the identification and evaluation of risks and opportunities, which includes the environmental element and a comprehensive process for the identification of environmental aspects of its processes, materials and services, to determine those that have or may have a significant impact on the environment, due to current and foreseeable future activities.
Environmental aspects include both those that are controlled by Madrileña Red de Gas (direct aspects) and those over whose management Madrileña Red de Gas does not exercise direct control, but may have a certain degree of influence from a life cycle perspective (indirect aspects). The aspects are classified into the following impact areas:
- Atmospheric emissions: ducted or non-ducted through chimneys.
- Waste: generated in warehouses, regulation and metering stations, satellite plants, works on distribution networks, etc.
- Consumption of natural and energy resources: water, electricity, fuels, etc.
- Other environmental aspects: this includes aspects related to nuisances such as noise, odours, spillages, etc.
- LPG Plants (61 visits)
- Emergencies (58 visits)
- Readings (47 visits)
- RMS (43 visits)
The number of reports with environmental incidents in the visits was 6. These correspond to incidents related to excessive vegetation or materials (waste) on the plants.
Furthermore, these on-site controls are complemented with documentary controls of the waste management records that must be included in the work files.
Both the identification and its evaluation are reviewed annually, thus ensuring that all significant aspects are under control and/or have the necessary actions to achieve it.
Our supplier approval, selection and monitoring processes ensure the transfer of our commitments to the environment (as described in detail in the chapter dedicated to our responsible management of the supply chain). In these processes, the necessary involvement and obligatory compliance with MRG’s commitments to the environment is conveyed through the approval and contracting requirements. Through a computer system, the contractors register all management and certification requirements. This information is monitored periodically by MRG.
Regarding the suppliers evaluated with environmental impacts, according to our environmental impact identification and analysis matrix, we have identified two types of significant negative risks (potential and actual) where supplier management is important: waste and leaks and spills.
Of a total of 29 suppliers evaluated and monitored, 20 have been identified as having a significant negative impact (70%). In no case has the relationship been terminated, although measures have been put in place to resolve the problems. Among the measures adopted in general, we have developed an operational control module in our digital process tool, which facilitates the monitoring of MRG.
In addition, throughout 2021 we have planned to work together with suppliers with a twofold objective: to strengthen environmental awareness and jointly define improvement actions.
During 2020, there have been no accidents with environmental impacts associated with fines or civil liability.
Madrileña Red de Gas has an on-line service through which it has up-to-date knowledge of all the environmental legislation applicable to its installations, and the implications derived from any regulatory changes.
5.2 Our Commitment in Figures
Madrileña has the digital process management tool of the Integrated Management System for the control of environmental indicators. These indicators are set into its scorecard.
The scorecard has control traffic lights that indicate the status of the indicator against the objectives set in the period. On a half-year basis, an in-depth analysis of the indicators and the degree of compliance is carried out, preparing reports that facilitate communication and take action when necessary.
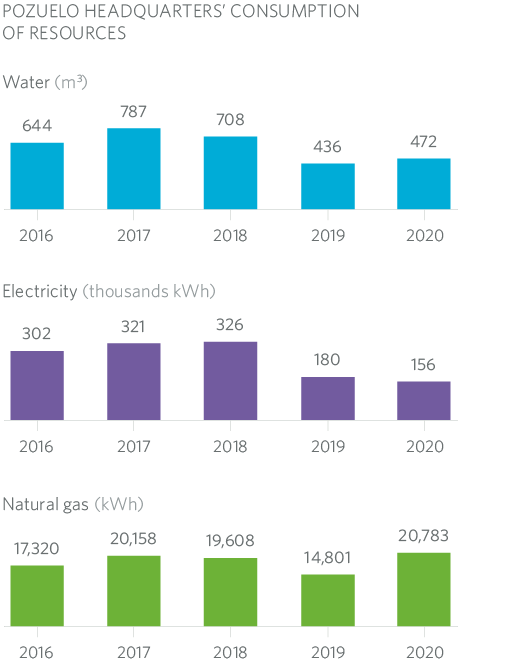
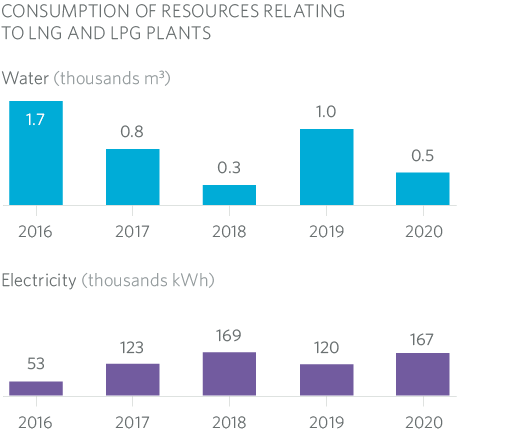
5.2.1 Resource Consumption
When analysing the indicators, it is important to bear in mind that during 2020 the operational staff, as well as all staff linked to the 24-hour emergency service, continued to use the MRG facilities in their day-to-day work, with the consumption of the buildings generally maintaining similar trends to previous years.
As far as electricity consumption is concerned, the trend shows how the different measures that are being taken are having an effect.
Water consumption in LPG plants is closely linked to the maintenance schedule, as well as plant decommissioning.
In accordance with RD 56/2016 Madrileña Red de Gas has carried out the energy audit both in 2016 and 2020.
As a result of these studies, the company has carried out various measures over the years aimed at reducing energy consumption.
- Lighting measures: from 2016 to the present, a process of replacing conventional lamps with LED lamps has been carried out, specifically fluorescent and halogen lamps have been replaced with LED lamps, the savings calculated after both audits have been 27,865 KWh per year.
- Air-conditioning measures, winter and summer temperatures settings, in accordance with RD 1826/2009. Estimated savings with these measures are 2,535 KWh per year.
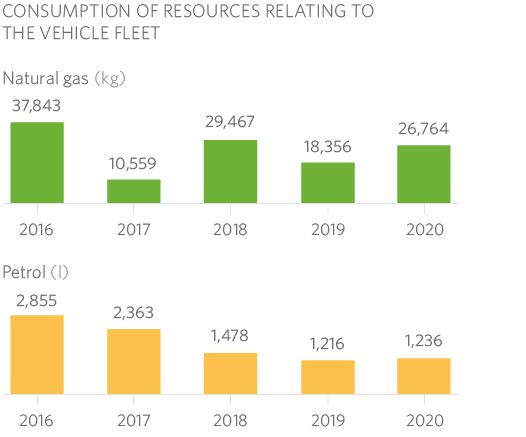
In recent years MRG has eliminated diesel vehicles from its fleet, gradually increasing the role of natural gas vehicles, with the clear objective of reducing emissions.
From 2017 to the present we are carrying out an important transformational PAPERLESS process.
After carrying out a survey to evaluate consumption in the different processes, a series of important measures have been implemented:
- Digitization of all field operations, designing mobility tools for the operators on which to record all the necessary data from their actions:
- Operations with clients: periodical inspections, home operations, meter verification, etc.
- Network operations: maintenance (works, leakage monitoring), emergencies, auxiliary installations, etc.
- Network Expansion Works.
- Digitization of the Company’s management processes: Financial (invoices, payment documents, expense receipts, etc.), Purchasing (commercial contracts), Human Resources (payments, communications, etc.), Risk Management (audit documents, inspections, files, reports, etc.).
- Paperless workstations.
- Change of paperwork habits: use of google drive for shared documents and work documents, promotion of the use of electronic resources, etc.
5.2.2 Atmospheric Emissions
MRG’s methodology for calculating fugitive methane emissions is aligned with event-based methodologies being used by other EU countries. Methodology agreed at sectoral level. During 2019 the methodology was revised and has been consolidated during this year.
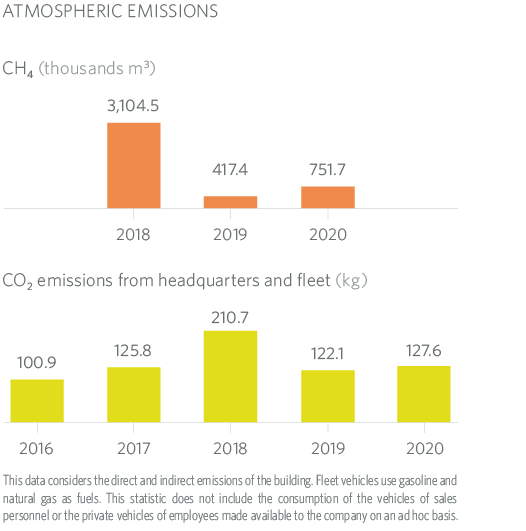
With this method the fugitive CH4 emissions are independent of pipe length. Taken into account are:
- Intrinsic emissions (leakage emissions due to holes or small cracks detected by the monitoring of the networks, to the permeation of the polyethylene and to leaks detected in the periodic inspections.
- Incidental emissions: by leaks due to damage, detected by own personnel or third parties, complaints or incidents, as well as common or building receptor leaks.
- Operational emissions.
The results obtained with this method are based on annually updated data reflecting best practices applied to network construction and maintenance, derived from the safety and environmental action plans carried out. Thus, the event-driven approach allows the design and application of improvement methods that contribute significantly to the reduction of methane emissions.
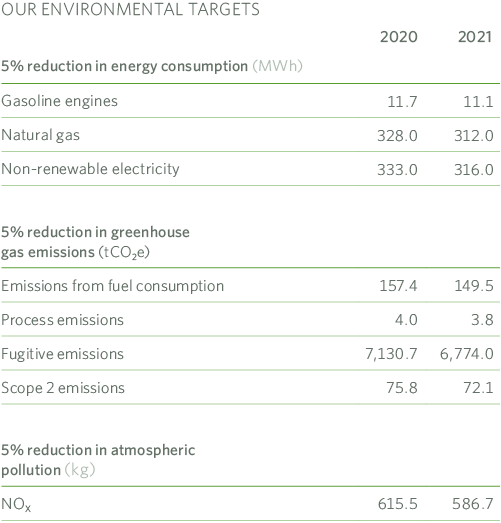
5.2.3 Carbon Footprint, Measurement and Commitment
Madrileña Red de Gas has a tool and procedure for calculating the carbon footprint for the activities associated with the Company, including direct Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, as well as indirect GHG emissions from the generation of electrical energy acquired and consumed. The measurement of the corporate carbon footprint allows us to know the Company’s environmental impact on climate change. The scope and limits employed in the calculation of the carbon footprint were as follows:
- Greenhouse gases to be included in the calculations: the main gases with the capacity to contribute to climate change and associated with the emission sources of Madrileña Red de Gas are included: CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs y PFCs.
- Emissions are quantified in tonnes of each of these gases and in tonnes of CO2 equivalent (CO2e).
- The infrastructures and resources included for the calculation, are:
- MRG Headquarters.
- Natural gas and LPG distribution network.
- LNG and LPG plants belonging to the distribution network.
- Fleet vehicles.
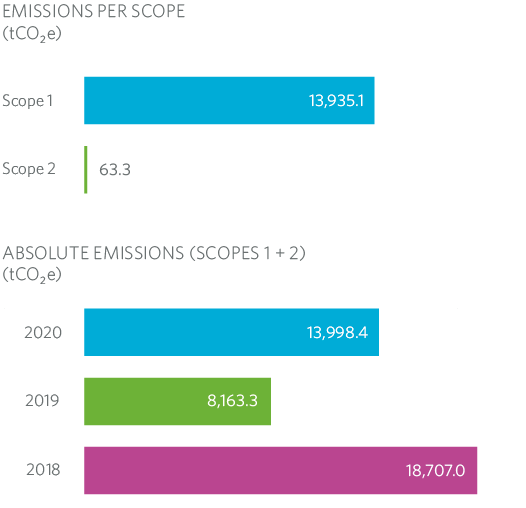
In order to calculate emissions, the EMEP/EEA and IPCC methodology is used, which makes it possible to estimate the quantity of emissions from each source based on quantifiable data (AD: activity data), as in the case of fuel consumption, and on specific coefficients (EF: emission factors) from contrasted sources such as EPA, IPCC, UNFCCC, COPEERT IV, etc. This methodology is in accordance with the methodological options contemplated in the UNE-ISO 14064-1 and in the guidelines of the Spanish Office for Climate Change (OECC).
In 2020 there was an upward change, caused by a very significant increase in monitored leaks accompanied by smaller increases in leaks due to damage to third parties and leaks due to emergency notifications.
If we make a comparison by type of scope, Scope 1 carbon footprint emissions are clearly the majority. And, as in previous years, fugitive emissions due to CH4 gas losses (96.3% of the total) that occur in pipes, connections and RMS of the network, and gas leaks due to damage to third parties, have played a major role in the final result.
5.2.4 Projects and investments to promote energy efficiency and reduce emissions
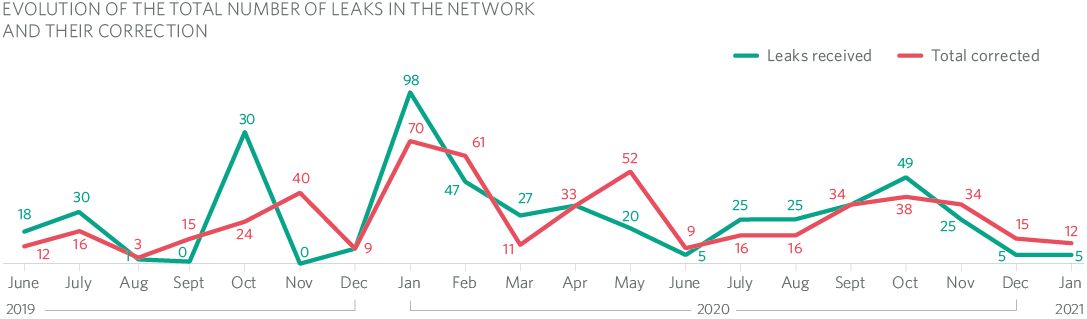
Distribution network monitoring
Since fugitive methane emissions are the most significant issue in our emissions and carbon footprint calculations, MRG maintains a permanently open tracking project.
This operation is aimed at detecting, locating, classifying and recording natural gas leaks in the supply network of the areas and auxiliary elements, as well as detecting other incidents in the network.
Systematic leakage monitoring is carried out on 100% of the line through which the pipeline runs.
An annual programme is designed, taking into account the historical data of the leakage rate of the networks and the materials that constitute them. The indicator used to evaluate a monitoring sector is the leakage index, which expresses the total number of leaks detected per km of network monitored, including those located both in the network and in service connections.
This identification and classification operation makes it possible to prioritize leakage elimination operations. In the event of leaks classified as level 1, the emergency control centre is notified immediately.
Production and use of renewable energies
Since 2019 MRG has installed a total of 158 panels at its offices in Virgilio Street, with a final power of 52.4 kWp.
The installation was designed for an annual generation of 86,860 MWh, since our average annual consumption is 285,432KWh.
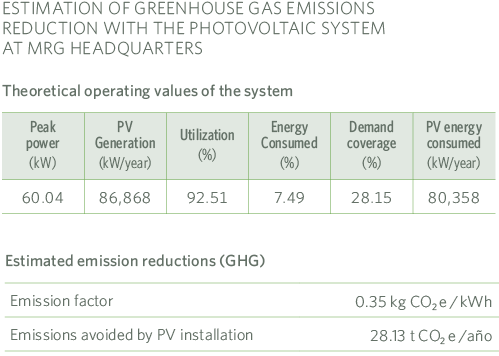
The energy generated by the PV installation does not involve the emission of CO2 into the environment, so the reduction in emissions is equal to the energy generated by the emissions factor considered (0.35).
The objective is the generation of clean energy in instantaneous self-consumption regime, without surplus, leak-proof. Allowing the management of surpluses stored in state-of-the-art lithium batteries, for use at night. This type of self-consumption is the most environmentally friendly.
Elimination of diesel fuel consumption
At MRG we have been phasing out diesel-powered vehicles from our fleet for years. We currently do not have any more. But we are not satisfied with this, and we have launched a new “MUS Plan” with a direct grant of 3,000 euros to all our employees who buy a vehicle that runs on CNG or who convert their own vehicle.
Since the scheme came into existence in 2018, in these three years 25 people have accessed the grants, and in MRG we have allocated 75,000 euros for this.
Innovative projects towards the use of clean energy
As we have already described in section 3.3. “Main challenges”, in MRG we are working on renewable gases (biomethane, hydrogen, synthetic gas) as cleaner alternatives for the future.
In addition, we are involved in innovative projects in the development of new urban spaces.
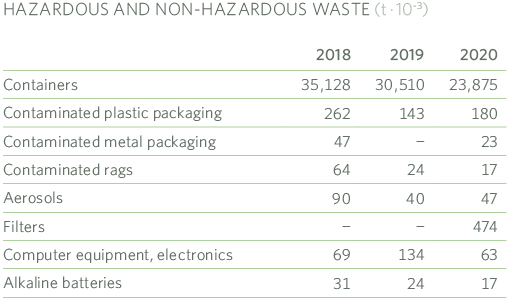
5.2.5 Waste
The management system addresses through its procedures and technical standards the control and management of waste, distinguishing its generation in work centres, during the operation and maintenance of the distribution network facilities, and construction and demolition works.
The processes meet the objective of minimization, for this we work from the design of the processes, operations, and the facilities themselves, optimizing the consumption of materials, promoting measures that favour recycling and reuse.
Recyclable waste such as meters are separated into aluminium and scrap. The different recoverable metallic materials are segregated and separated from each other, then grouped into different scrap according to material and quality, in order to facilitate their transport to the smelting plants and thus to reprocess them.
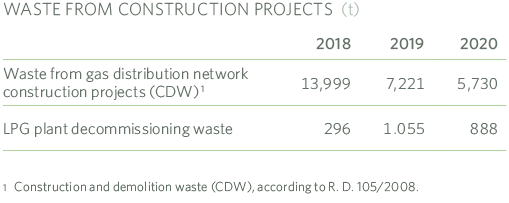
The treatment of waste from the dismantling of LPG plants logically depends on the number of plants dismantled, specifically 118 plants in 2020 and 130 in 2019, all of them with their associated environmental documentation dossier.
The Project Management present on site for the dismantling of LPG plants makes a great effort to monitor the waste generated and compliance with environmental regulations.
The Project Management carries out, among other tasks:
- Supervision of contractors’ waste management plans.
- Compilation of waste management documentation.
The area responsible for these works in MRG, together with the collaboration of the Project Management, compiles all the documentation related to the management of waste from the contractor companies.
In addition, the Project Management issues non-conformity notices if deviations are detected, in order to eliminate the possible deviation.
Use of land from dismantling LPG tanks
- The land is replaced with material and soil of similar characteristics to the rest of the area.
- Materials that can be reused (e.g. vaporizers, extinguishers, regulators) are transported to MRG’s warehouses.
- The stored materials are collected by a recycling company.
- Demolition waste is delivered to an authorised manager for recovery or landfill.
Use of water in the maintenance and dismantling of LPG plants
Water is stored and reused in the same process as long as the characteristics of the water allow it, minimizing consumption and reducing the production of contaminated water.
5.3 Biodiversity
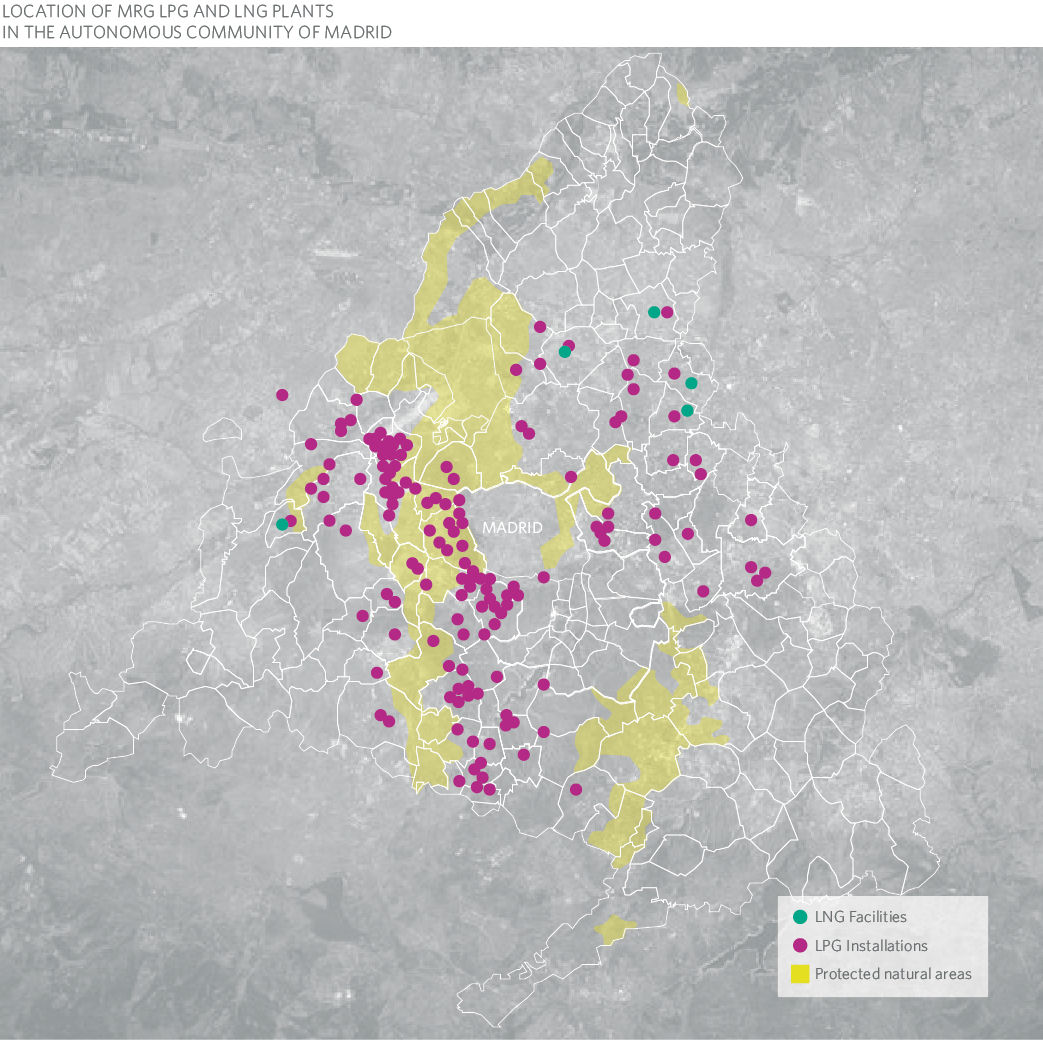
Madrileña Red de Gas, in its commitment to biodiversity, works to avoid the siting of its installations in protected areas or areas of high ecological value, although its raison d’être of bringing gas to where it is needed, within the Community of Madrid, makes the presence, albeit minimal, of installations in these areas inevitable.
Conserving biodiversity means managing our relationship with nature in a sustainable way for ourselves and future generations. To this end, it promotes its preventive and corrective measures when necessary.
In compliance with legislation, we have identified the facilities located in or bordering protected or high-value areas, assessed the risks of impact on the areas and established actions to control the risk.
We currently have 169 LPG installations with above ground and underground tanks, of which 12 are affected by the SEVESO III Directive (lower level). 85% of the plants are located in urban environments, some of them next to natural areas. Only 18 plants are found within Protected Natural Spaces. Specifically, 16 facilities are located within the Cuenca Alta del Río Manzanares Regional Park and one in the Curso Medio del Río Guadarrama Regional Park and its surroundings.
Our 5 liquefied natural gas plants, LNG, are located in natural areas next to urbanized areas, none of them located in protected natural spaces. We have 6,196 Km of natural gas distribution in the Community of Madrid, with 206 regulation and metering stations (RMS), of which 10 are in protected areas, specifically 8 in the Cuenca Alta del Manzanares Regional Park and 2 in the Curso Medio del Río Guadarrama Regional Park and its surroundings.
For the facilities located in these protected areas, the inventory of habitats of community interest has been carried out using the GEOPORTAL MAPAMA tool of the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food. It also applies to installations located in areas bordering these protected areas. The priority habitats inventoried in general in these facilities are:
- Substeppe areas of grasses and annuals of the Thero-Brachypodietea (Habitat code 6220).
- Mediterranean temporary ponds (Habitat code 3170).
- Endemic forests of Juniperus spp. (Habitat code 9560).
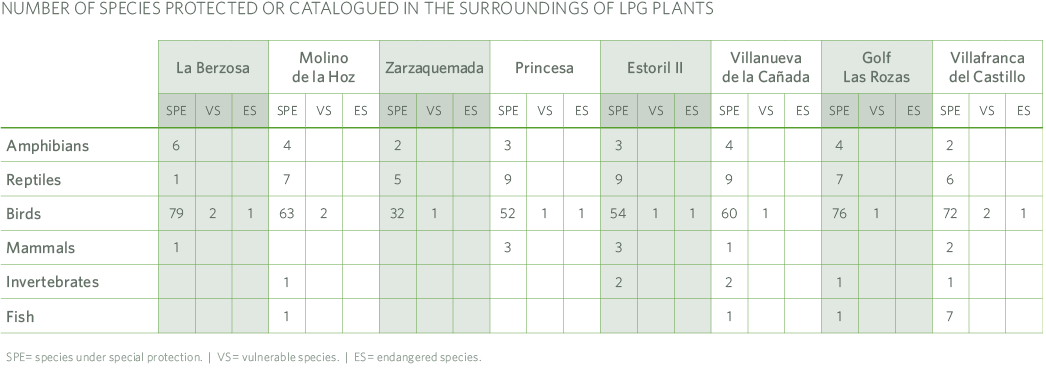
The species that appear on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List are also identified, distinguishing the different species and their classification: species under special protection (SPE), vulnerable species (VS) and endangered species (ES). Generally speaking, we can talk about species of special protection, especially birds. There are very few cases of vulnerable and endangered species.
The aforementioned facilities are affected by Law 26/2007 of 23 October on Environmental Responsibility and all the required administrative procedures have been complied with, it having been necessary to establish specific financial guarantees for 3 of these facilities, Villafranca del Castillo, La Berzosa and Villanueva de la Cañada.
Following its work methodology, Madrileña Red de Gas has identified the aspects and impacts on the environment derived from the presence of its installations in different stages: construction, maintenance, possible modification and dismantling, assessing the risks and applying the necessary protection or mitigation measures. The identification takes into account the direct and indirect aspects of the processes associated with the life cycle of the facilities, as well as the potential consequences arising from hypothetical accidents and/or incidents. Once identified, they are subjected to evaluation in order to understand the significant aspects and take the necessary actions.
This evaluation for direct aspects is carried out by assessing three variables: toxicity (T), receiving environment (RE) and quantity (Q). In the case of indirect aspects, toxicity and the receiving environment are taken into account. For the potential aspects, the variables of frequency (of the occurrence of the event) and the severity of the consequences are considered. For this purpose, standardised valuation criteria are used in the Company, obtained through the work and consensus of the different Business Units. All this is included in a management system procedure under the standard UNE-EN ISO 14001:2015. It is important to note that this analysis is reviewed annually.
The existence of small leaks is an unavoidable element, although they are repaired at the time of detection and there are means for the prevention and control of the emergency.
Regarding the analysis of potential aspects, we summarize in the table the result indicating the aspects evaluated as significant.
The result of the analysis entails a set of actions to ensure risk control. Specifically for this type of aspect, the actions are as follows:
- Training and awareness of our own staff and of the contractor company that works in the installations, promoting commitment from small habits or practices to operate with care and respect, acting consciously and responsibly. During 2020, due to the pandemic, no such awareness-raising activities were carried out; they are planned for 2021.
- Ensure the environmental commitment of the contracted companies through the purchasing processes, as developed in the chapter on the supply chain.
- Processes, procedures and standards for the management and control of waste, installation cleaning work, etc. for the different phases of the life cycle of the installations, compliance with which is mandatory for in-house personnel and contractor companies, especially noteworthy being the mechanisms for the on-site control of construction and demolition waste and the tracking of the inerting water from the tanks of the LPG plants that are dismantled.
- Implementation of an IT tool (through the digital management software of the Integrated Management System processes) on which it will be compulsory and easily controllable to record all waste management processes.
- Operational control visits during the works, and documentary controls, analysing and taking the necessary measures when non-compliance is detected.
During 2020 we have decommissioned 6 LPG plants located in protected areas, all of them located in the Cuenca Alta del Manzanares Regional Park, representing a total of 545 m2 of recovered surface area.
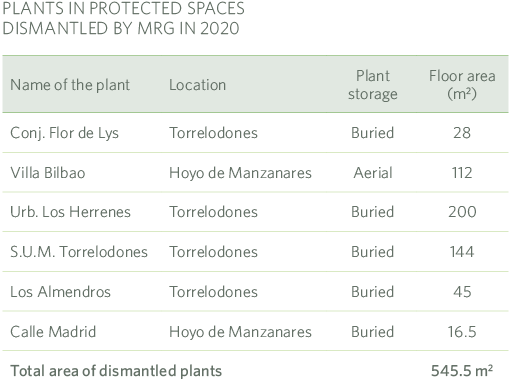
Every construction site, in this case for dismantling, has a Site Manager appointed by MRG, who is responsible for approving the construction and demolition waste management plan developed by the contractor at the start of the works and for signing the final works certificate.
MRG hires an external company to collect data and, where appropriate, samples for the drafting of the mandatory report on the closure of contaminated soils. These reports are submitted to the Competent Authority of the Community of Madrid, which issues an administrative resolution in this regard.

